腎臓の状態を知るためのIDEXXのソリューション
腎機能は、患者の全体的な健康状態を把握する上で極めて重要な役割を果たします。しかし、症状が現れていない状態で管理をするのは困難です。IDEXXの検査と技術により、患者の腎臓の状態を明らかにし、確かな自信を持って早期介入と治療を行うことができます。

診断ソリューション
腎臓の評価および治療のモニタリングに有用な検査で、より良い患者のケアが可能になります。

早期に、より深い知見の提供を。
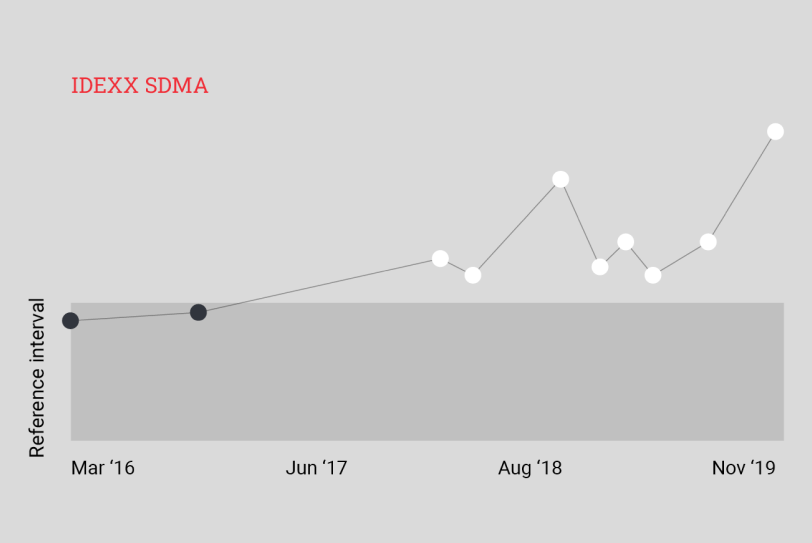
IDEXX SDMA検査
SDMAは院内または検査サービスにおいて、クレアチニン検査では見逃されてしまう軽度から中度の腎機能の低下をいち早く発見できます。1–3
血液化学検査スクリーニングにSDMAを追加することで、患者の疾患の有無に関わらず、原発性の腎臓病や、合併症によって引き起こされる腎機能の低下の早期発見に大きな価値を発揮します。2–14

これまで不可能だった尿細管障害の発見が可能に。
IDEXX 尿中シスタチンB
尿中シスタチンB がIDEXXの腎臓関連検査に加わったことで、より包括的に腎臓を評価できるようになりました。これによって、これまで以上に正確に、活動性の腎障害や急性腎障害を発見できるようになります。尿中シスタチンB は症状のある犬猫向けの尿検査で、臨床兆候の有無にかかわらず、尿細管障害を検出できます。

リン過剰を未然に防止。
IDEXX FGF-23検査
IDEXX FGF-23検査は、慢性腎臓病(CKD)を患う猫におけるリン過剰の管理とモニタリングのための、まったく新しい手法です。現在、CKDを患う猫におけるIRISの治療提案でも推奨されています。15
IDEXX FGF-23検査は、確信を持って食事改善などの治療提案を行えるようにし、IRIS CKDステージ1および2の猫における代謝性骨疾患の早期発見を可能にします。16,17

知見をより完全なものに。
包括的な尿検査とUPC
包括的な尿検査と尿蛋白:クレアチニン(UPC)比は、より詳細な腎臓の健康状態の把握に役立ちます。また、尿比重(USG)は、腎機能バイオマーカーと合わせて解釈をすることで、水和状態や腎機能に関する必要な情報を提供してくれます。さらに、UPC比を同時に検査すると、CKDの診断と治療に役立つ可能性もあります。包括的な尿検査は、自信を持って患者の腎臓の健康状態を評価する上で不可欠です。
ツールとテクノロジー
患者に合わせた知見から個々のベースラインまで、IDEXXの進化し続けるツールとテクノロジーにより、院内または検査センターの結果と併せて自信を持った意思決定に必要な情報を提供します。
すべての患者が異なるように、ベースラインも異なります。
ベットコネクトプラス
単独での検査結果は重要性が高いものの、比較対象が無いためにその価値は限定されてしまいます。そのため、定期的な腎臓の健康状態のモニタリングは、患者の疾患の有無や若年高齢に関わらず欠かせません。ベットコネクトプラスがあれば、患者ごとのベースラインの確立、傾向の特定、病歴の確認をすべて一ヵ所で行うことができます。
参考資料
- Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, Yerramilli M, Jewell DE. Comparison of serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine as kidney function biomarkers in cats with chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2014;28(6):1676–1683. doi:10.1111/jvim.12445
- Nabity MB, Lees GE, Boggess MM, et al. Symmetric dimethylarginine assay validation, stability, and evaluation as a marker for early detection of chronic kidney disease in dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2015;29(4):1036–1044. doi:10.1111/jvim.12835
- Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, Yerramilli M, Almes K, Jewell DE. Serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine in dogs with naturally occurring chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2016;30(3):794–802. doi:10.1111/jvim.13942
- Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, Yerramilli M, Yu S, Jewell DE. Comparison of serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine as kidney function biomarkers in healthy geriatric cats fed reduced protein foods enriched with fish oil, L-carnitine, and medium-chain triglycerides. Vet J. 2014;202(3):588–596. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2014.10.021
- Nabity MB. Traditional renal biomarkers and new approaches to diagnostics. Toxicol Pathol. 2018;46(8):999–1001. doi:10.1177/0192623318800709
- Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, Li J, Yerramilli M, Jewell DE. Serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine in cats with kidney stones. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0174854. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174854
- Burton W, Drake C, Ogeer J, et al. Association between exposure to Ehrlichia spp. and risk of developing chronic kidney disease in dogs. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2020;56(3):159–164. doi:10.5326/JAAHA-MS-7012
- Dahlem DP, Neiger R, Schweighauser A, et al. Plasma symmetric dimethylarginine concentration in dogs with acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2017;31(3):799–804. doi:10.1111/jvim.14694
- Drake C, Coyne M, McCrann DJ, Buch J, Mack R. Risk of development of chronic kidney disease after exposure to Borrelia burgdorferi and Anaplasma spp. Top Companion Anim Med. 2021;42:100491. doi:10.1016/j.tcam.2020.100491
- Szlosek D, Robertson J, Quimby J, et al. A retrospective evaluation of the relationship between symmetric dimethylarginine, creatinine and body weight in hyperthyroid cats. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0227964. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0227964
- Yerramilli M, Farace G, Quinn J, Yerramilli M. Kidney disease and the nexus of chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury: the role of novel biomarkers as early and accurate diagnostics. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2016;46(6):961–993. doi:10.1016/j.cvsm.2016.06.011
- Mack RM, Hegarty E, McCrann DJ, Michael HT, Grauer GF. Longitudinal evaluation of symmetric dimethylarginine and concordance of kidney biomarkers in cats and dogs. Vet J. 2021;276:105732. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2021.105732
- Michael HT, Mack RM, Hegarty E, McCrann DJ, Grauer GF. A longitudinal study of the persistence of increased creatinine and concordance between kidney biomarkers in cats and dogs. Vet J. 2021;276:105729. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2021.105729
- Data on file at IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine USA.
- International Renal Interest Society. Announcement of changes to IRIS guidelines. Accessed February 8, 2023. www.iris-kidney.com/guidelines/guidelines_updates_2023.html
- Geddes RF, Elliott J, Syme HM. The effect of feeding a renal diet on plasma fibroblast growth factor 23 concentrations in cats with stable azotemic chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2013;27(6):1354–1361. doi:10.1111/jvim.12187
- Geddes RF, Biourge V, Chang Y, Syme HM, Elliott J. The effect of moderate dietary protein and phosphate restriction on calcium-phosphate homeostasis in healthy older cats. J Vet Intern Med. 2016;30(5):1690–1702. doi:10.1111/jvim.14563
- Data on file at IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine USA. Individual results will vary based upon each patient’s case complexity and practitioner’s IRIS CKD staging experience.
www.idexx.com/en/veterinary/reference-laboratories/sdma/sdma-iris/#vetconnectplus